National
Discharged gay troops ready to re-enlist
‘That’s the life I was destined to lead’

For Thomas Cook, deciding whether or not to re-enlist in the U.S. military after “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” is off the books is a no-brainer.
Cook, a Houston resident who was discharged in 2004 under the anti-gay law, said he “absolutely” plans to rejoin the armed forces on the day that the military’s gay ban is lifted.
“That’s the life I was destined to lead,” Cook said. “I think military service is in my blood and my past experience in the military — I absolutely loved it. I wouldn’t have changed anything about it. I come from a family of military people, and I’m looking forward to going back into the military as soon as I can — Sept. 20.”
Cook, now 29, said he doesn’t intend to enter the same field in the military that he held upon his discharge, nor will he enter the same branch of service. He served in military intelligence in the Army prior to his separation, but Cook said he plans to join the Air Force nursing field to make use of the education he has since received in that area.
On July 22, President Obama, Defense Secretary Leon Panetta and Chairman of the Joint Chief of Staff Adm. Mike Mullen certified that the U.S. military is ready for open service in accordance with the repeal law signed in December, starting the 60-day period for when “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” will be a thing of the past on Sept. 20.
Gay service members discharged under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” will be able to re-enter the armed forces from that point forward. Some service members whose separations received media attention said their affinity for military service leaves no doubt in their mind that they’ll re-enter the military as soon as possible.
Cook, who first joined the Army in 2001, said he feels compelled to continue military service even though he was kicked out after he declared his sexual orientation. In 2003, the team leader in Cook’s company said during a training exercise he’d kill anyone in his crew whom he found out was gay. Cook reported the team leader’s remarks to his battalion commander and said the threat alarmed him because he is gay. The confession started Cook’s discharge proceedings, and he was ultimately separated from the Army under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” on Jan. 20, 2004.
Seeking to rejoin the military, Cook was lead plaintiff in Cook v. Gates, a lawsuit challenging “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” that was filed by Servicemembers Legal Defense Network. However, the U.S. District Court in Massachusetts and the U.S. First Circuit Court of Appeals upheld the constitutionality of “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” in response to the challenge, forcing Cook to wait for legislative repeal before he could re-enter the military.
Cook said he bears no ill-will toward the military even though he was expelled from his position simply for stating his sexual orientation and was unable to reclaim his role through the litigation in which he was lead plaintiff.
“The organization itself has the policy in place, but the people I worked with didn’t necessarily believe in the policy,” Cook said. “I worked with people and the other soldiers that believe the same things I believed, which is anyone and everyone that is eligible to serve and is capable of serving should be allowed.”
Other service members whose discharges received prominent attention also said they intend to rejoin the armed forces after the gay ban is lifted — but aren’t feeling the same need to re-enlist on Sept. 20 as soon as “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” is off the books.
Alex Nicholson, executive director of Servicemembers United, is planning to re-enter the military as a member of the Reserves and, after obtaining a law degree, pursue a career as a military lawyer in the Judge Advocate General’s Corps.
“It’s still a lifestyle and a set of people that I am comfortable around and I’ve always had an affinity for,” Nicholson said. “It’s hard to explain the phenomenon and the fraternity that it is.”
Like Cook, Nicholson plans to take a different position than his previous role. Nicholson was an Army intelligence officer prior to his separation at the age of 20 under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” in 2002. A fellow service member outed him to his unit after she read a letter he had written in Portuguese to a man he dated before he joined the Army.
After forming Servicemembers United in 2005, Nicholson became active in the discussion with the White House and Congress that led to legislative repeal of “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell.” Nicholson was also the sole named plaintiff in the lawsuit Log Cabin Republicans v. United States, which led the U.S. Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals to institute an injunction this year barring further discharges under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell.”
Despite his plan to rejoin the military, Nicholson, now 30, said he plans to hold off on re-enlisting for about two or three years as he continues his advocacy work because he doesn’t believe being in the military while acting as a watchdog for gay troops is appropriate.
“I just don’t feel like I would be able to continue to do the job that I do by doing that,” Nicholson said. “That’s going to add a whole additional layer of complexity to the political work, or the watchdog work that we do, if I were to do something like that.”
Also planning to re-enlist is Mike Almy, a former Air Force communications officer who was discharged under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” in 2006. He said he wants back in the armed forces because he has an affinity for it.
“It’s what I’ve done for 13 years,” Almy said. “I miss it, the people, the camaraderie, the mission and want to finish my career.”
After a fellow service member read a private e-mail revealing his sexual orientation and reported the information to his commander, Almy was discharged under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell.” He never made a public statement that he was gay, but was nonetheless separated.
Almy, 40, received significant attention as a service member discharged under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” after testifying before the Senate Armed Services Committee last year against the military’s gay ban and taking on tough questioning from Sen. John McCain (R-Ariz.).
The best path that Almy said he sees for re-entering the armed forces is the resolution of the lawsuit in which he is lead plaintiff, Almy v. United States. The case, filed by SLDN and pending before the U.S. District Court of Northern California, seeks to reinstate him and other plaintiffs in the armed forces.
The case, Almy said, represents his best chance to return to the Air Force as an officer because of difficulties in the path ahead if he were to re-enlist at a recruiting station.
“It’s very difficult as an officer to go back on active duty, and that has absolutely nothing to do with ‘Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell,’ but just the fact that being separated and out for a couple years — coupled with the fact that there’s a drawdown — so that’s why we got the lawsuit in the works,” Almy said.
Almy added he’s expecting a resolution to the lawsuit in a couple of months and not the exact same position he held upon discharge, but a position that is comparable and the same rank.
Upon his discharge under “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell,” Almy lost all the benefits he would have had if he had been allowed to retire on his own accord. His reinstatement in the armed forces would enable him to reclaim those benefits.
“I have none whatsoever,” Almy said. “That’s what we’re trying to get as well. Assuming we’re successful in the lawsuit and win, and get reinstatement, then we’ll pick up where we left off basically, so I’ll get those benefits, go on to finish my career and ultimately retire.”
Federal Government
UPenn erases Lia Thomas’s records as part of settlement with White House
University agreed to ban trans women from women’s sports teams

In a settlement with the Trump-Vance administration announced on Tuesday, the University of Pennsylvania will ban transgender athletes from competing and erase swimming records set by transgender former student Lia Thomas.
The U.S. Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights found the university in violation of Title IX, the federal rights law barring sex based discrimination in educational institutions, by “permitting males to compete in women’s intercollegiate athletics and to occupy women-only intimate facilities.”
The statement issued by University of Pennsylvania President J. Larry Jameson highlighted how the law’s interpretation was changed substantially under President Donald Trump’s second term.
“The Department of Education OCR investigated the participation of one transgender athlete on the women’s swimming team three years ago, during the 2021-2022 swim season,” he wrote. “At that time, Penn was in compliance with NCAA eligibility rules and Title IX as then interpreted.”
Jameson continued, “Penn has always followed — and continues to follow — Title IX and the applicable policy of the NCAA regarding transgender athletes. NCAA eligibility rules changed in February 2025 with Executive Orders 14168 and 14201 and Penn will continue to adhere to these new rules.”
Writing that “we acknowledge that some student-athletes were disadvantaged by these rules” in place while Thomas was allowed to compete, the university president added, “We recognize this and will apologize to those who experienced a competitive disadvantage or experienced anxiety because of the policies in effect at the time.”
“Today’s resolution agreement with UPenn is yet another example of the Trump effect in action,” Education Secretary Linda McMahon said in a statement. “Thanks to the leadership of President Trump, UPenn has agreed both to apologize for its past Title IX violations and to ensure that women’s sports are protected at the university for future generations of female athletes.”
Under former President Joe Biden, the department’s Office of Civil Rights sought to protect against anti-LGBTQ discrimination in education, bringing investigations and enforcement actions in cases where school officials might, for example, require trans students to use restrooms and facilities consistent with their birth sex or fail to respond to peer harassment over their gender identity.
Much of the legal reasoning behind the Biden-Harris administration’s positions extended from the 2020 U.S. Supreme Court case Bostock v. Clayton County, which found that sex-based discrimination includes that which is based on sexual orientation or gender identity under Title VII rules covering employment practices.
The Trump-Vance administration last week put the state of California on notice that its trans athlete policies were, or once were, in violation of Title IX, which comes amid the ongoing battle with Maine over the same issue.
New York
Two teens shot steps from Stonewall Inn after NYC Pride parade
One of the victims remains in critical condition
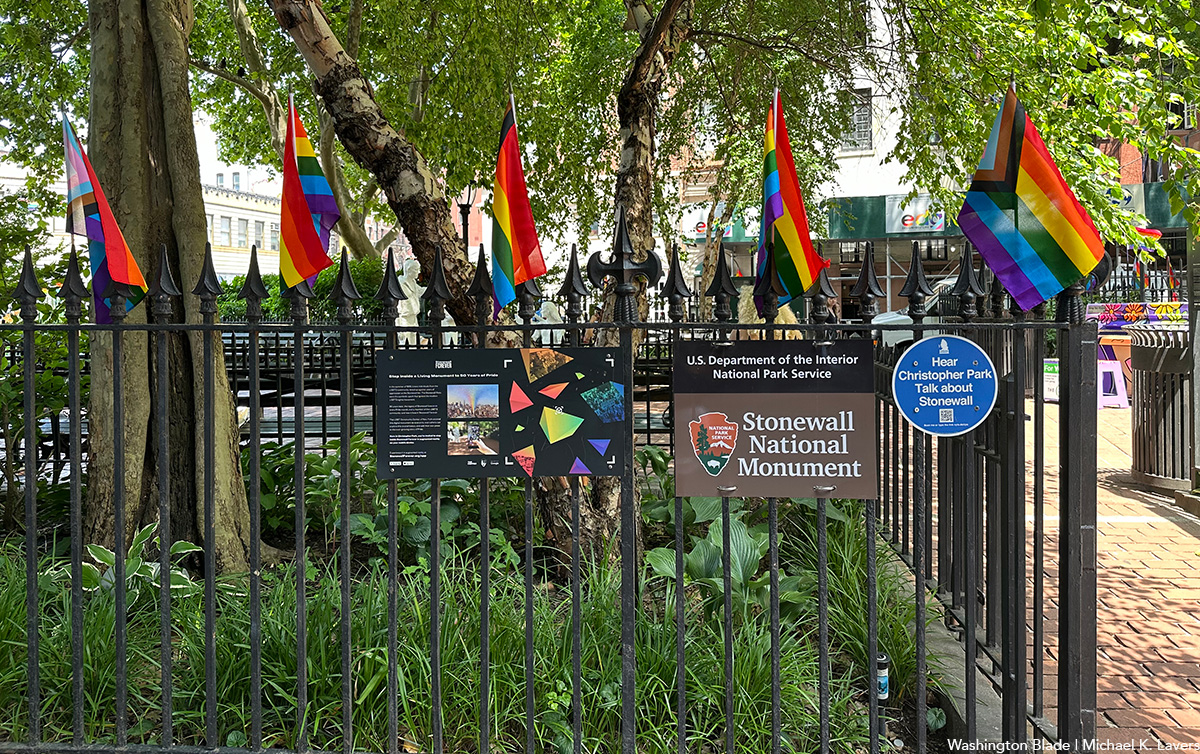

On Sunday night, following the annual NYC Pride March, two girls were shot in Sheridan Square, feet away from the historic Stonewall Inn.
According to an NYPD report, the two girls, aged 16 and 17, were shot around 10:15 p.m. as Pride festivities began to wind down. The 16-year-old was struck in the head and, according to police sources, is said to be in critical condition, while the 17-year-old was said to be in stable condition.
The Washington Blade confirmed with the NYPD the details from the police reports and learned no arrests had been made as of noon Monday.
The shooting took place in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Manhattan, mere feet away from the most famous gay bar in the city — if not the world — the Stonewall Inn. Earlier that day, hundreds of thousands of people marched down Christopher Street to celebrate 55 years of LGBTQ people standing up for their rights.
In June 1969, after police raided the Stonewall Inn, members of the LGBTQ community pushed back, sparking what became known as the Stonewall riots. Over the course of two days, LGBTQ New Yorkers protested the discriminatory policing of queer spaces across the city and mobilized to speak out — and throw bottles if need be — at officers attempting to suppress their existence.
The following year, LGBTQ people returned to the Stonewall Inn and marched through the same streets where queer New Yorkers had been arrested, marking the first “Gay Pride March” in history and declaring that LGBTQ people were not going anywhere.
New York State Assemblywoman Deborah Glick, whose district includes Greenwich Village, took to social media to comment on the shooting.
“After decades of peaceful Pride celebrations — this year gun fire and two people shot near the Stonewall Inn is a reminder that gun violence is everywhere,” the lesbian lawmaker said on X. “Guns are a problem despite the NRA BS.”
New York
Zohran Mamdani participates in NYC Pride parade
Mayoral candidate has detailed LGBTQ rights platform

Zohran Mamdani, the candidate for mayor of New York City who pulled a surprise victory in the primary contest last week, walked in the city’s Pride parade on Sunday.
The Democratic Socialist and New York State Assembly member published photos on social media with New York Attorney General Letitia James, telling followers it was “a joy to march in NYC Pride with the people’s champ” and to “see so many friends on this gorgeous day.”
“Happy Pride NYC,” he wrote, adding a rainbow emoji.
Mamdani’s platform includes a detailed plan for LGBTQ people who “across the United States are facing an increasingly hostile political environment.”
His campaign website explains: “New York City must be a refuge for LGBTQIA+ people, but private institutions in our own city have already started capitulating to Trump’s assault on trans rights.
“Meanwhile, the cost of living crisis confronting working class people across the city hits the LGBTQIA+ community particularly hard, with higher rates of unemployment and homelessness than the rest of the city.”
“The Mamdani administration will protect LGBTQIA+ New Yorkers by expanding and protecting gender-affirming care citywide, making NYC an LGBTQIA+ sanctuary city, and creating the Office of LGBTQIA+ Affairs.”
-

 U.S. Supreme Court4 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court4 days agoSupreme Court upholds ACA rule that makes PrEP, other preventative care free
-

 U.S. Supreme Court4 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court4 days agoSupreme Court rules parents must have option to opt children out of LGBTQ-specific lessons
-

 Television4 days ago
Television4 days ago‘White Lotus,’ ‘Severance,’ ‘Andor’ lead Dorian TV Awards noms
-

 Music & Concerts4 days ago
Music & Concerts4 days agoBerkshire Choral to commemorate Matthew Shepard’s life