Health
New D.C. HIV cases decline by widest margin in 5 years: report
City offering free home test kits to counter decline in clinic visits
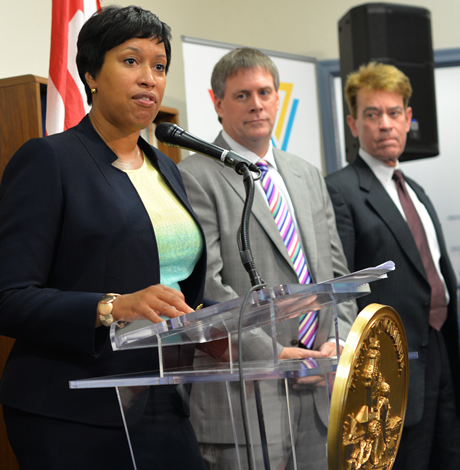


The number of new HIV infections reported in D.C. in 2019 declined by 16 percent from 2018, the largest decline over the previous five years, indicating the city’s HIV prevention efforts are moving closer to achieving Mayor Muriel Bowser’s goal of ending the AIDS epidemic in the nation’s capital, according to a report released last week by the D.C. Department of Health.
The 2019 HIV data, which also show the city has met the mayor’s goal of ensuring that 90 percent of city residents with HIV know their HIV status by 2020, were released on Aug. 20 as part of the health department’s annual 2019 HIV, Sexually Transmitted Disease, Hepatitis, and Tuberculous Epidemiology and Surveillance Report.
The report shows the number of newly diagnosed HIV cases in D.C. decreased from 335 in 2018 to 282 in 2019, a 16 percent drop. The report notes that the 2019 figure of 282 new HIV cases represents a 79 percent decline from the 1,374 new cases reported in 2007.
DOH officials have said the decline in new cases appeared to have leveled off and reached a plateau between 2015 and 2018 when the number of new cases remained relatively stable. From 2015 to 2016, the new cases went from 399 to 379, a 5 percent decrease. The number of new cases from 2016 to 2017 dropped from 379 to 371, a decline of just 2 percent.
The new cases from 2017 to 2018 went from 371 to 335, a 9 percent decrease, the DOH report shows.
According to DOH officials, including DOH Director Dr. LaQuandra Nesbitt, the 16 percent decline from 2018 to 2019 is an indication that stepped up efforts are working to encourage people to seek out the HIV prevention drug known as PrEP and for people who are HIV positive to become virally suppressed through medication that’s 99 percent effective in preventing transmission of the virus to someone else.
The report released last week says that among the D.C. residents newly diagnosed with HIV in 2019, 59 percent were “virally suppressed” with medication within 90 days of their diagnosis. It says that was an improvement from the 45 percent that were virally suppressed within 90 days after diagnosis in 2018.
“However, this indicates that not enough people are getting on HIV treatment timely to attain viral suppression,” a DOH statement accompanying the release of the report says.
DOH Officials said HIV data for 2020 will not be released until August of 2021. But the officials nevertheless disclosed they observed a downward change in the number of people being tested for HIV from 2019 to the first half of 2020.
Michael Kharfen, senior deputy director for DOH’s HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis, STD, and TB Administration, told the Washington Blade that DOH has found that fewer people in D.C. in 2020 have been tested for HIV compared to this time last year.
Kharfen said restrictions and concerns related to the coronavirus pandemic are believed to be the main reason fewer D.C. residents are showing up this year at HIV testing sites offered by DOH, private community clinics, or doctors’ offices. He said DOH has responded to this development by offering free home HIV test kits to anyone who requests them by contacting DOH online or by phone.
Kharfen said the free test kits can be obtained through a special DOH website at: getcheckeddc.org.
“D.C. Health recognizes that the COVID-19 pandemic is changing the way D.C. residents obtain medical care and other services,” Nesbitt said in the DOH statement. “We are expanding telehealth options and home-based testing to give residents the opportunity to take charge of their health,” she said.
The 2019 DOH report includes these additional findings:
• There are 12,408 current D.C. residents, or 1.8 percent of the population, who are living with HIV. Black and Latino residents with HIV exceeded 1 percent of their respective populations, with Black residents disproportionately impacted at 2.8 percent.
• There were just two babies born with HIV in D.C. in 2019.
• “Men who have sex with men and heterosexual contact are the two leading modes of transmission reported among newly diagnosed and identified HIV cases.”
• More than half of people living with HIV in D.C. are 50 years old and older. Young people ages 13 to 24 represent nearly 20 percent of new HIV diagnoses between 2015 and 2019. The number of “new HIV cases among young people between the ages of 20-24 remained level for the past three years.”
• The number of “newly diagnosed HIV cases attributable to injection drug use decreased by 99 percent from 150 cases in 2007, prior to the scale up of D.C.’s needle exchange program, to 2 cases in 2019.
• In 2019, there were 9,337 cases of chlamydia, 4,374 cases of gonorrhea, and 297 cases of primary and secondary cases of syphilis reported in D.C.
• There were 1,099 people with newly reported hepatitis C in D.C. in 2019.
• There were 24 cases of newly reported tuberculosis in D.C. in 2019, a 33 percent decline from the 36 newly reported cases in 2018.
“Our partnerships with the community have continued to yield promising results to both stem and reduce new HIV cases, while also delivering better and more efficient treatment to residents living with HIV,” Mayor Bowser said in the DOH statement.
“Our goal of ending the HIV epidemic in D.C. is not yet done, and we will continue to work to ensure equity in services, reduce stigma as an access barrier, making testing easier, support needle exchange, and keep people HIV negative,” the mayor said.
Jewel Addy, a spokesperson for Whitman-Walker Health, one of D.C.’s largest private health centers that provides HIV and other medical services for the LGBTQ community, said Whitman-Walker saw a 63 percent decline in its HIV testing between January and July of this year compared to that same period in 2019.
Addy said Whitman-Walker has seen about a 62 percent decline during that same period in the number of sexually transmitted infections testing it has offered at its various offices. Whitman-Walker discontinued in-person office visits at most of its locations except for COVID-19 tests in the past several months, but Addy said in-person visits have been resumed for HIV and COVID testing in several of Whitman-Walker’s offices this summer.
Health
Choose U ambassadors share lived experiences with HIV, personal reflections, and insights

The Choose U World AIDS Day panel brought together three longtime advocates living with HIV to talk about care, stigma, and what living with HIV over the long-term means to them. The conversation featured Jahlove Serrano, Joyce Belton, and Andrew Nichols, who have each lived with HIV for more than 20 years. News is Out hosted the event in partnership with Gilead Sciences.
“Co-created with community representatives from around the world, Choose U is comprised of inspiring examples of how the outlook for aging with HIV has dramatically changed,” Gilead shared in the recent launch of the program. “By focusing on the real-world experiences of people in different circumstances, Choose U spotlights individuals prioritizing starting and staying on HIV treatment, self-care, and overall strategies to help them lead healthier lives.”
The Choose U ambassadors opened with a clear message: Lived experience drives understanding.
Each panelist talked through the decisions, relationships, and periods of uncertainty that shaped their HIV care. They also described their approaches to HIV treatment and adherence, including the importance of staying on treatment to help lower the risk of HIV drug resistance. They reflected on the shifts they have seen in HIV treatment over the decades, the value of honest conversations with providers, and how staying engaged in care and on HIV treatment helped them lead longer, healthier lives.
The panel discussed U=U, which stands for “Undetectable equals Untransmittable.” Undetectable means there is so little virus in the blood that a lab test can’t measure it. Research shows that taking HIV treatment as prescribed, and getting to and staying undetectable, prevents HIV from spreading through sex.
The panelists also spoke about the emotional side of living with HIV over the long-term and the stigma they have faced. Joyce described a personal moment when her pastor visited her in the hospital and how that experience began her work educating her church community about HIV.
Jahlove talked about how his biological family reacted to his diagnosis. “When I disclosed my status, they told me that I put a shame on the family,” said Jahlove. When he shared his status with his peers, they responded with support, which gave him a sense of empowerment.
Andrew, a professional therapist, described how he has experienced stigma in dating and in his workplace, and why he turns to therapy for guidance. “Therapy has really helped me rebuild my confidence and realize my self-worth has to come from me,” said Andrew. “Then after that, I can help with the greater community.”
The panel closed with a message for others living with HIV: They encouraged viewers to start and stay engaged in HIV treatment and care, ask questions, and rely on supportive networks. Their stories show how starting and staying on treatment over the long-term, community, and affirmation can shape well-being.
A recording of the full 30-minute event is now available on YouTube, which you can access here.
Health
The harsh truth about HIV phobia in gay dating
HIV and stigma remain baked into queer dating culture

Uncloseted Media published this article on Dec. 9.
This story was produced with the support of MISTR, a telehealth platform offering free online access to PrEP, DoxyPEP, STI testing, Hepatitis C testing and treatment and long-term HIV care across the U.S. MISTR did not have any editorial input into the content of this story.
By SAM DONNDELINGER | In his room, 19-year-old Cody Nester toggles between Grindr profiles on his phone.
As he senses chemistry with a match, he knows he has to flag something that could be a deal breaker.
“Did you see on my profile that I’m HIV positive?” he writes.
The reply arrives instantly.
“You’re disgusting. I don’t know why you’re on here.” Seconds later, the profile disappears, suggesting Nester is blocked.
“He went out of his way to say that. People could at least be more aware, ask questions, and understand the reality [of living with HIV] instead of attacking us,” Nester told Uncloseted Media.
“I would say 95 percent of people respond that way,” says Nester, who lives in Hollywood, Fla., and works at a Mexican restaurant. “The entire conversation is going fine. They’re down to meet up and then right when I mention [HIV], it’s always, ‘Oh no, never mind.’”
Some other messages he’s received include:
“You’ll never get anything in your life.”
“Why don’t you die?”
“Why are you on here?”
More often, it’s silence, a cold “No” or a sudden block.
“It’s like you’re a white fish in a school of black fish,” he says. “You’re immediately the odd one out.”
Even though Nester’s undetectable status makes it impossible for him to transmit HIV to partners during sex, he experiences stigma around HIV, something which nearly 90 percent of Americans agree still exists, according to a 2022 GLAAD report. And a survey shared in 2019 found that 64 percent of respondents would feel uncomfortable having sex with someone living with HIV, even on effective treatment. The emotional cost of this stigma is a significant barrier to intimacy and can result in a loss of self-esteem, fear of disclosure and suicidal thoughts.
What the science says — and why it doesn’t seem to matter
“The fear comes from antiquated ideas around HIV,” says Xavier A. Erguera, senior clinical research coordinator at University of California, San Francisco,’s Division of HIV, Infectious Diseases & Global Medicine. “A lot of people who are newly diagnosed still fear it’s a death sentence. Even though we have medications now to treat it effectively, and it’s basically a chronic condition, people haven’t caught up.”
Since 1996, antiretroviral therapies have developed to where they can suppress the virus to levels so low that it is undetectable in the blood, and thus not able to be transmitted to sexual partners. This is known as Undetectable = Untransmittable, or U=U. According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report from 2024, 65 percent of HIV-positive cases are virally suppressed.
Another line of defense is pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), which reduces the risk of acquiring HIV from sexual intercourse by roughly 99 percent when taken as prescribed. Approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012, the medication launched as a once-a-day pill and was hailed as a breakthrough as it transformed the sex lives of gay men, which had been shaped by decades of fear about HIV complications and about where AIDS came from.
“Internal logic doesn’t reflect what we know scientifically,” says Kim Koester, associate professor in the Department of Medicine at UCSF. “I was very optimistic when PrEP came out. The drug works, so why wouldn’t everyone use it?”
Even with PrEP use on the rise, less than 600,000 Americans used it in 2024, and Koester says skepticism and judgments about taking the drug persist.
“The phobia is pervasive,” Koester told Uncloseted Media. “People believe that others get the disease because of their lifestyle. … PrEP was supposed to be the antidote to the threat of HIV, reduce the anxiety, and make you more open to who you are and the sex you want. It’s supposed to be liberating. It is part of the answer. But it’s not enough. We don’t have enough people using PrEP for it to make the dent in the stigma we need.”
According to a 2023 study of seven informants living with HIV, public stigma stems from problematic views from society that those living with HIV are “a dangerous transmission source,” “disgraceful” and “violators of social and religious norms who have committed deviant behavior.”
Laramie Smith, assistant professor of Global Public Health at the University of California, San Diego, says this stigma is unwarranted and fueled by misunderstanding:
“With today’s treatments, it shouldn’t be a life-altering identity shift. It should be no different than, ‘I have diabetes.’ If you’re virally suppressed, it shouldn’t matter whether you’re friends with someone, whether you’re sleeping with someone — the science shows us that.”
How HIV phobia shows up online
Nester, who contracted HIV last year from a Grindr hook-up who insisted he was negative, says he is just starting to accept his diagnosis. “I didn’t go back on the apps for a long time after that. It messed with my mental health … realizing I’d have to take medication for the rest of my life.”
Since he started dating again this year, returning to apps like Grindr and Sniffies, he has faced a new normal. He tries to do everything “right” and disclose his status early. Even on his Grindr profile, he identifies as “poz,” slang for HIV-positive.
Still, he says most people ghost him once they find out. “The second I bring it up, it’s ‘No,’” says Nester. “The amount of discrimination you get … it’s always the same pattern. … People don’t know, and they don’t want to know. It messes with you.”
This discrimination may be fueled by a deprioritization of HIV awareness programs across the country. Earlier this month, the U.S. State Department did not commemorate World AIDS Day for the first time in 37 years. HIV prevention programs have been slashed, especially in conservative districts, and only 25 states and D.C. require both HIV and sex education. In many states, health curricula often lag behind current science and omit teaching about PrEP, gay sex and concepts like U=U. Research shows that Gen Z is currently the least educated generation about HIV.
“I could go all day explaining HIV, but people don’t want to listen,” says Nester, who is part of Gen Z. “People don’t want to learn about it; they just want to avoid it.”
HIV anxiety and public stigma shaped by history
Even in more progressive areas, stigma still exists. Damian Jack, a 45-year-old from Brooklyn, remembers sitting in an exam room in 2009 as a doctor explained how low his T-cell count was, which is a hallmark of HIV infection.
“I started hysterically crying,” he told Uncloseted Media. “HIV meant death. That’s what I thought.”
In 1981, when Jack was 1 year old, the first reports of a mysterious and deadly immune deficiency syndrome, which would later be named AIDS, appeared in the U.S. Growing up, Jack saw countless terrifying images of men on their deathbeds with Kaposi sarcoma, the purple lesions the media once called “gay cancer.” Public misinformation and fearmongering spread ideas that AIDS was a disease that “only gay men and drug users get.” And politicians often equated it with homosexuality and moral failure, calling it a “gay plague.” It wasn’t until September 1985, four years after the crisis began and thousands had died, that President Ronald Reagan first publicly mentioned AIDS.
Decades later, the emotional residue of that era and the shame associated with the virus lingers.
Hours after learning of his diagnosis, Jack faced his first encounter with rejection. He already had a date planned that night, and his doctor and friends encouraged him to go.
They had a great time until the date asked him: “Are you negative or positive?”
He told the truth.
“It was just understood there wouldn’t be a second date,” says Jack. “I remember thinking, ‘This is how dating is going to be now.’ I felt so anxious telling guys. It followed me everywhere. I don’t think that anxiety ever truly goes away.”
The emotional impact of HIV stigma
For those who are HIV-negative, experts say that “stigma’s whole design is to ‘other.’”
“The ‘us versus them’ creates that false sense of safety when it comes to HIV,” says Smith. “If I can believe that someone did something to deserve their diagnosis, and I’m not that [kind of person], then I’m safe.”
This othering is painful and can lead to shame, fear and isolation, and it is linked to a higher risk of depression and anxiety.
“If I’m undesirable, and that’s what those messages are communicating, that threatens your sense of safety, your sense of belonging and the fundamental desire we all have to be loved,” Smith says. “And that starts to reinforce the thinking that ‘I am not worthy. This virus that I have means that I’m not lovable. I am not safe showing up among other men.’”
“I pretend it doesn’t hurt, but some things do sting a little bit,” Nester says. “You start thinking, ‘Am I really that disgusting? Am I really that singled out?’”
When public stigma turns inward
“Internalized stigma is what occurs when applying the stereotypes about who gets HIV, the prejudice, the negative feelings, onto yourself,” says Smith.
In 2024, 38 percent of people living with HIV reported internalized stigma. And studies show that it can predict hopelessness and lower quality of life, even when people are engaged in care or virally suppressed.
Internalized stigma can also affect how people practice safe sex and communicate about the virus. A 2019 survey of men who have sex with men found that individuals who perceived greater community-level stigma were less likely to be aware of — and use — safer-sex functions available on dating apps, such as HIV-status disclosure fields, as well as sexual health information and resources.
“[HIV phobia] is probably the most intense, subvert bigotry I think you could experience,” Joseph Monroe Jr., a 48-year-old living in the Bronx, told Uncloseted Media.
On dating apps, men have messaged him things like, “You look like you’ve got that thing” and “Go ahead and infect someone else.”
Monroe has also dealt with misinformed people who rudely opine about how he contracted the virus: “Who fucked you? That’s how you got it, right?” people will say to him.
“You end up internalizing all these stereotypes about who gets HIV — that you were promiscuous, that you didn’t care about yourself, that you did something wrong,” says Smith. “You carry that in, and then you have to relearn: ‘No, I didn’t. This is just a health condition.’”
What HIV acceptance looks like and raising awareness
For those living with HIV, acceptance feels far away.
“You’re living under this threat of HIV and the threat that others find you threatening. It inhabits you socially and sexually,” Koester says. “People are hunkering down. Not putting themselves out there and having a mediocre quality of life. To have a sense of empowerment, you have to be legitimate and seen in the world and it’s hard to do that with the stigma that exists.”
Researchers say the path forward lies as much in conversation as in medicine.
Koester says she talks about HIV and PrEP anywhere she can, including in salons, cafes and restaurants. “Whenever I get into a cab with someone, I’m going to bring up HIV so the driver gets accustomed to hearing about it. … We have a long way to go in terms of exposure and awareness and every little bit helps.”
Part of this lies in increasing awareness through targeted marketing campaigns. PrEP is still profoundly misunderstood outside major urban centers, with uneven uptake among minority groups and usage gaps in the Bible Belt. And a 2022 U.S. survey found that 54.5 percent of people living with HIV didn’t know what U=U meant, and less than half of Americans agree that people living with HIV who are on proper medications cannot transmit the virus.
While eradicating stigma is slow, there is hope for acceptance.
Years after Jack’s diagnosis, in 2021, he told a man he was on a third date with that he was HIV-positive but undetectable. His date’s reply was almost casual:
“Oh — is that it? I thought you were going to say you had a boyfriend or something. I’m on PrEP. You’re fine.”
“It felt so good to hear him say that and accept me,” says Jack. “I was like, ‘This is my person. You’re my person.’” One year later, they got married.
Back in Florida, 19-year-old Cody Nester isn’t feeling this acceptance. He still scrolls past profiles that read “Only negative guys” and tries to ignore the hateful messages.
“It still hurts, but I know it’s coming from fear,” he says. “I wasn’t too informed about HIV before I got it. … When I got it, I really jumped into the rabbit hole and began to learn. I really do think [HIV and stigma] is because people are not knowledgeable. … When people don’t know details, they tend to get scared.”
Additional reporting by Nandika Chatterjee.
Health
Developing countries to receive breakthrough HIV prevention drug at low cost
Announcement coincided with UN General Assembly

Philanthropic organizations on Wednesday announced two agreements with Indian pharmaceutical companies that will allow a breakthrough HIV prevention drug to become available in developing countries for $40 a year per patient.
The New York Times notes Unitaid, the Clinton Health Access Initiative, and Wits RHI reached an agreement with Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories to distribute lenacapavir. The Gates Foundation and Hetero brokered a separate deal.
Unitaid, the Clinton Health Access Initiative, Wits RHI, and the Gates Foundation announced their respective agreements against the backdrop of the U.N. General Assembly.
Lenacapavir users inject the drug twice a year.
UNAIDS in a press release notes lenacapavir in the U.S. currently costs $28,000 a year per person.
“This is a watershed moment,” said UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima in a statement. “A price of USD 40 per person per year is a leap forward that will help to unlock the revolutionary potential of long-acting HIV medicines.”
The State Department earlier this month announced PEPFAR will distribute lenacapavir in countries with high HIV prevalence rates. A press release notes Gilead Sciences, which manufactures the drug, is “offering this product to PEPFAR and the Global Fund at cost and without profit.”