Africa
LGBTQ rights group sues Kenya police chief over anti-gay protests
Mombasa demonstrations began after ruling allowed NGO to register

An advocacy group in Kenya has sued Police Inspector General Japhet Koome for allowing religious leaders and lobby organizations to hold homophobic protests whenever court rulings favor the LGBTQ community.
Two petitioners — Mr. JM and the Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation — have sued Koome in the High Court in Mombasa, the country’s second largest city, and demanded a “ban on anti-LGBTQ protests in the country.”
The petitioners’ move is in response to recent anti-LGBTQ protests, particularly in Mombasa after last month’s Supreme Court ruling that affirmed its February decision in support of the National Gay and Lesbian Rights Commission and its ability to register as an NGO.
The controversial ruling sparked criticism from clerics, politicians and the general public. Demonstrations the two petitioners have described as gross human rights violations against the LGBTQ community followed.
An MP from the ruling party and Mohamed Ali — a celebrated investigative journalist whose anti-gay motion for the government to ban public discussion, reporting and distribution of LGBTQ content in the country passed overwhelmingly in Parliament — are among those behind the homophobic Mombasa protests.
Six LGBTQ lobby groups applauded the rulings as a “crucial shot in the arm towards LGBTQ rights” and condemned protest organizers for “mobilizing towards hatred and marginalizing others.”
Mr. JM and CMRSL have also sued two anti-LGBTQ activists and a national lobby group dubbed the “Anti-LGBTQ Movement” that organized the demonstrations, in addition to the police official whose office authorizes street marches by issuing permits to protesters.
“The petitioners have sought to include new amendments to the petition filed last week via the court’s online filing system and they have until Oct. 11 when the court will give directions to the hearing of the case,” a source familiar with the petition told the Washington Blade.
To stop any future homophobic protests, the petitioners want the court to declare the LGBTQ community is also entitled to constitutional rights and freedoms without hate or discrimination just like their opposite-sex counterparts.
They argue the anti-LGBTQ protests, characterized by incitement to violence in March and last month in response to the Supreme Court’s rulings, have led to increased cases of homophobia and threats to the lives of the queer community across the country.
The petitioners claim the “Anti-LGBTQ Movement” group has been propagating “violence, elimination and expulsion” of the queer community from the country in its relentless homophobic campaign. They further allege that organizations working with LGBTQ people have recorded “more than 100 cases of violence, forced evictions and denial of services” by landlords, employers and the public as a result of these protests.
The petitioners also claim the protests have led to the shutting down of “more than 20 organizations and medical facilities” that provide essential HIV and STI treatment services to LGBTQ people because of security concerns.
Mr. MJ and CMRSL in their case have included the Kenya National Commission on Human Rights, a state-funded watchdog organization, as an interested party, although it always distances itself from defending LGBTQ rights.
The Kenyan Constitution, which only recognizes consensual opposite-sex relations, directs the KNCHR. Section 162 of the penal code criminalizes consensual same-sex sexual relations.
This sidelining has forced the LGBTQ community to demand a representative to the KNCHR to represent their interests, such as intersex people who are represented after a landmark law that recognizes them as Kenya’s third sex, took effect in July 2022. The petitioners did not engage KNCHR before listing it as an interested party.
The state-funded National Cohesion and Integration Commission, Amnesty International Kenya and the Kenya Human Rights Commission are among the other institutions the two petitioners have included in the case as interested parties.
Amnesty International Kenya with Irungu Houghton as its executive director on Sept. 30 held the “State of Freedoms and Rights in 2023” conference in partnership with United States International University Africa in Nairobi, the Kenyan capital. Participants demanded respect for the rights of every person, including members of the LGBTQ community.
The rights organization vowed to fight any infringement of the rights of any person or group, regardless of their gender or sexual orientation, in line with its newly launched 4-year strategic framework for 2024-2028 that will guide its human rights advocacy.
Meanwhile, some parents in one of Kenya’s all female high schools are angry after administrators suspended 18 students who allegedly engaged in what they described as lesbianism.
The students’ suspension from Cardinal Otunga Girls’ High School in the western part of the country last week has caused fury among their parents, because they are set to start taking their final high school national exams on Oct. 10. This action comes amid the government’s plans to consider a recommendation from a presidential task force on education reforms to hire imams and chaplains in schools to guide students against what they feel is the infiltration of LGBTQ practices.
Africa
Lesbian South African MP named to country’s new Cabinet
Steve Letsike won a seat in the National Assembly on May 29
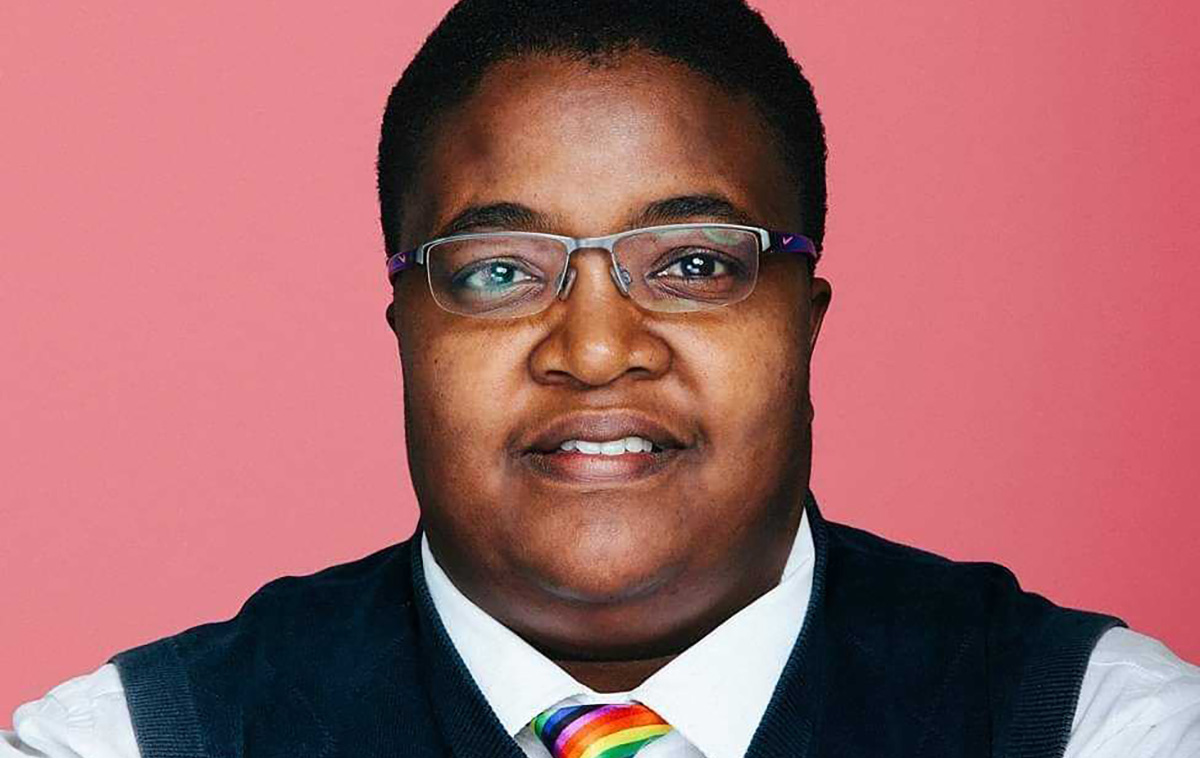

South African President Cyril Ramaphosa on Sunday appointed lesbian MP Steve Letsike to his Cabinet.
Letsike, founder of Access Chapter 2, a South African advocacy group who is a member of the African National Congress that Ramaphosa leads, will be the country’s deputy minister of women, youth, and people with disabilities.
Letsike won a seat in the South African National Assembly in national and provincial elections that took place on May 29.
The ANC lost its parliamentary majority that it had had since Nelson Mandela in 1994 won the South African presidency in the country’s first post-apartheid elections. Ramaphosa on Sunday announced Letsike and other new Cabinet members after the ANC and nine other parties agreed to form a National Unity Government.
The Washington Blade has reached out to Letsike for comment.
Africa
Congolese justice minister orders prosecutor general to arrest LGBTQ allies
Constant Mutamba issued directive on June 15, implementation unclear
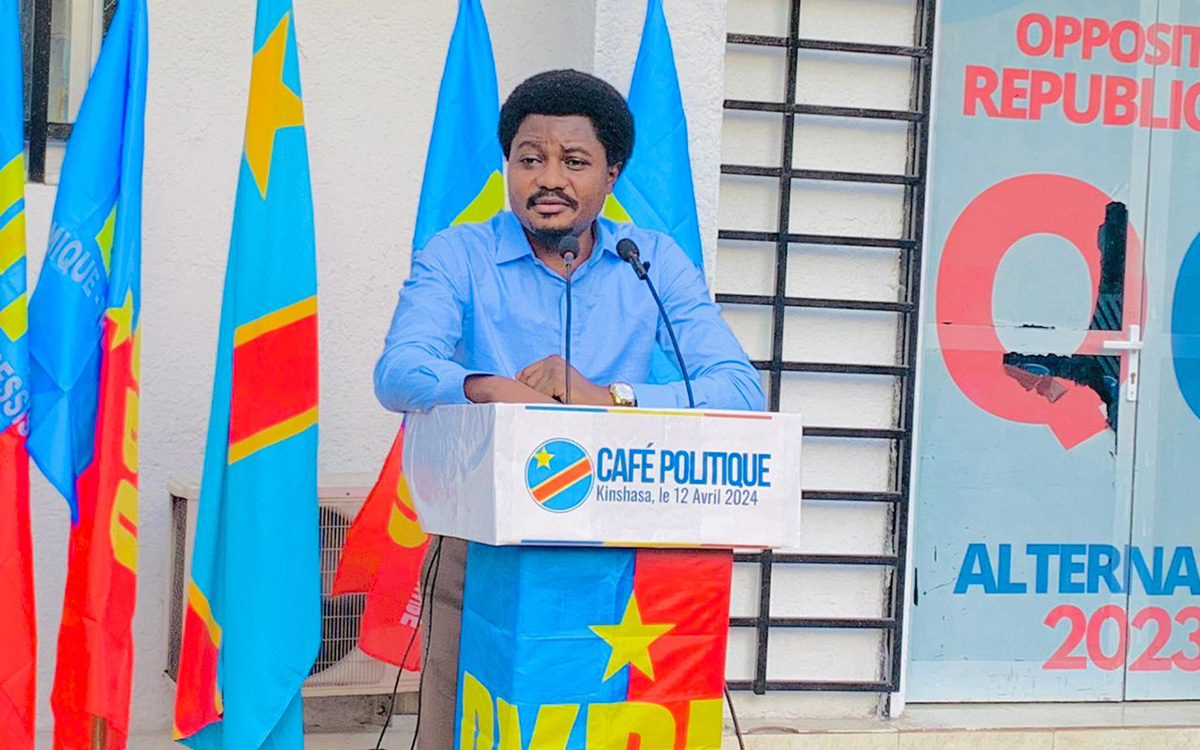

Congolese Justice Minister Constant Mutamba has instructed his country’s prosecutor general to arrest LGBTQ allies.
The newly appointed justice minister in a June 15 communique said the prosecutor general should initiate legal proceedings against people who advocate for the LGBTQ community in Congo.
Although same-sex marriages are constitutionally prohibited, there is currently no law that criminalizes consensual same-sex sexual relations. The communique has raised a lot of eyebrows from social and LGBTQ activists who are asking on what grounds Mutamba issued the communique.
“He could have started by initiating a bill in this direction, but in the current Congolese legislation he is missing the point,” said Jean Claude Katende, a Congolese human rights activist who is the president of the African Association of Human Rights. “If he wants to repress homosexuals, he must initiate a law which must make this behavior an offense and have it punished. He will be arrested for complicity in arbitrary arrests. The constitution is clear, no one can be prosecuted for an act which does not constitute an offense.”
Khelver Hermano, a Congolese social commentator, said the law should not be interpreted based on one person’s emotions.
“LGBT marriage is already not applied in the DRC but the minister wants to incarcerate those who do it informally without a legal basis,” said Hermano. “The law is not interpreted according to our will.”
“Does the penal code in the DRC recognize polygamy? Why don’t we arrest all these known polygamists?” asked Hermano. “Just as polygamists are not prosecuted, we cannot do so against LGBT people.”
Many Congolese people, however, have welcomed the communique, arguing same-sex relations are un-African and unorthodox.
Article 172 of the country’s penal code states a person “who commits a moral crime by exciting, facilitating or promoting to satisfy the passions of others, debauchery or the corruption of persons of either sex under or apparently under the age of 21 years shall be punishable by a prison term of three months to five years or a fine.” Article 176 says a person “who engages in activities against public decency shall be punishable by a prison term of eight days to three years and/or a fine.”
Although not entirely applicable, the prosecutor general can use these two penal code articles to initiate the arrests — the country in recent years has seen some arrests of LGBTQ people.
The June 15 communique is not the first time Mutamba has come out against the LGBTQ community.
Mutamba earlier this year introduced a bill that would criminalize acts of homosexuality. The proposal received widespread support, particularly on social media where many Congolese people described it as a turning point for the country and for the continent at large.
Although parliament has not formally debated the bill, activists are concerned it will pass without many major objections because most MPs have previously said they do not support the LGBTQ community. It remains unclear how the prosecutor general will executive Mutamba’s communique.
Africa
Prominent South African activist elected to country’s parliament
Steve Letsike founded Access Chapter 2

A prominent South African LGBTQ activist has won a seat in the country’s parliament.
Steve Letsike, a lesbian woman who founded Access Chapter 2, a South African advocacy group, is a member of the African National Congress. She is also part of the ANC’s National Executive Committee that determines the party’s direction.
Letsike won a seat in the South African National Assembly in national and provincial elections that took place on May 29.
The ANC lost its parliamentary majority that it had had since Nelson Mandela in 1994 won the South African presidency in the country’s first post-apartheid elections. MPs earlier this month re-elected President Cyril Ramaphosa after the ANC invited the Democratic Alliance and other parties to form a Government of National Unity.
Letsike in a statement to the Washington Blade described her election as “a milestone for the people of South Africa, and also affirmative of our party’s posture that is inclusive and intention to transformation agenda.”
“I am not in parliament for myself but the people that trusted the ANC to send individuals that will put people first,” said Letsike. “In that cohort that includes the LGBTI people like myself. Rooted in the teaching of a just society, that seeks equality and believes in the rule of law. That demand on developmental agenda from a queer lens and clear priorities of the people is important.”
“I am delighted by this task, trust and hope for our people,” she added.
-

 Canada1 day ago
Canada1 day agoToronto Pride parade cancelled after pro-Palestinian protesters disrupt it
-

 Theater4 days ago
Theater4 days agoStephen Mark Lukas makes sublime turn in ‘Funny Girl’
-
 Baltimore3 days ago
Baltimore3 days agoDespite record crowds, Baltimore Pride’s LGBTQ critics say organizers dropped the ball
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoHaters troll official Olympics Instagram for celebrating gay athlete and boyfriend











